The TLDR
The short explanation of single rail and multi rail is that both are a different way to design the same thing : a device that supplies power to your computer. Internally, you have some differences. But they are completely transparent to the end-user and do not change how you use your PC (at least as long as you plug your cables correctly on a multi-rail unit).
The difference is on the 12V rail, which powers your CPU, GPU, and a few other minor parts of the computer (but seriously 95% of the 12V rail is almost always CPU and GPU).
A single-rail unit has one big 12V output to handle everything in the whole system.
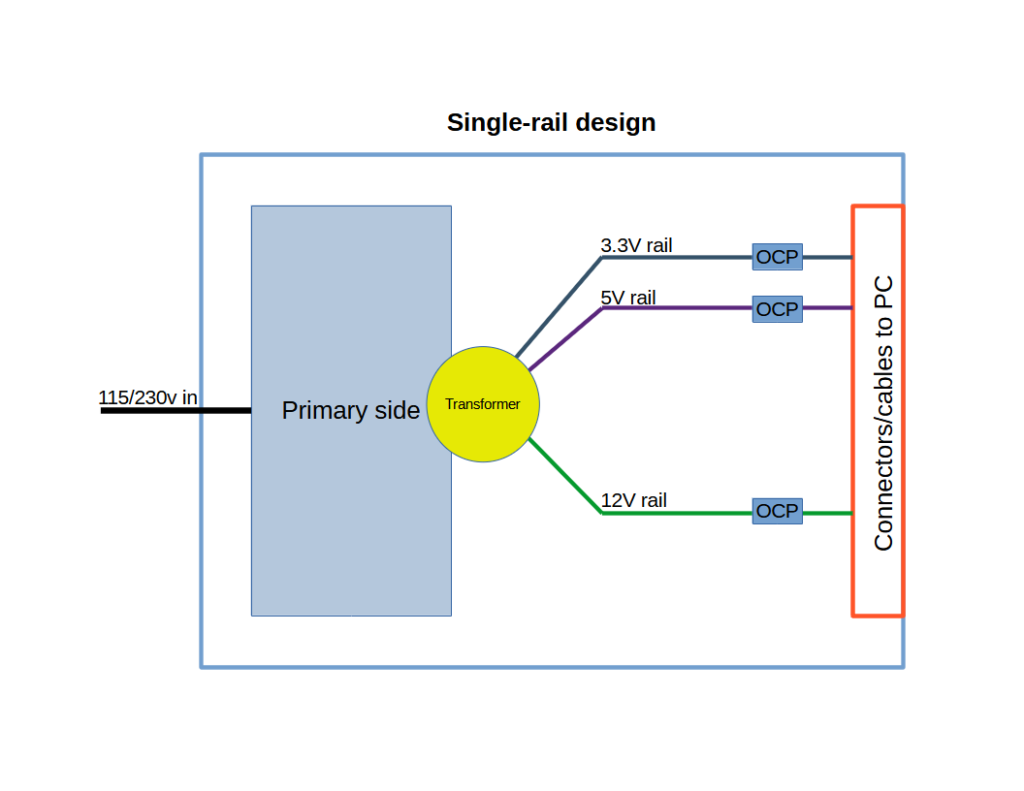
A multi-rail unit can have 2 or more smaller 12V outputs, and the user is expected to balance each part of the computer on different rails to not overload a rail.
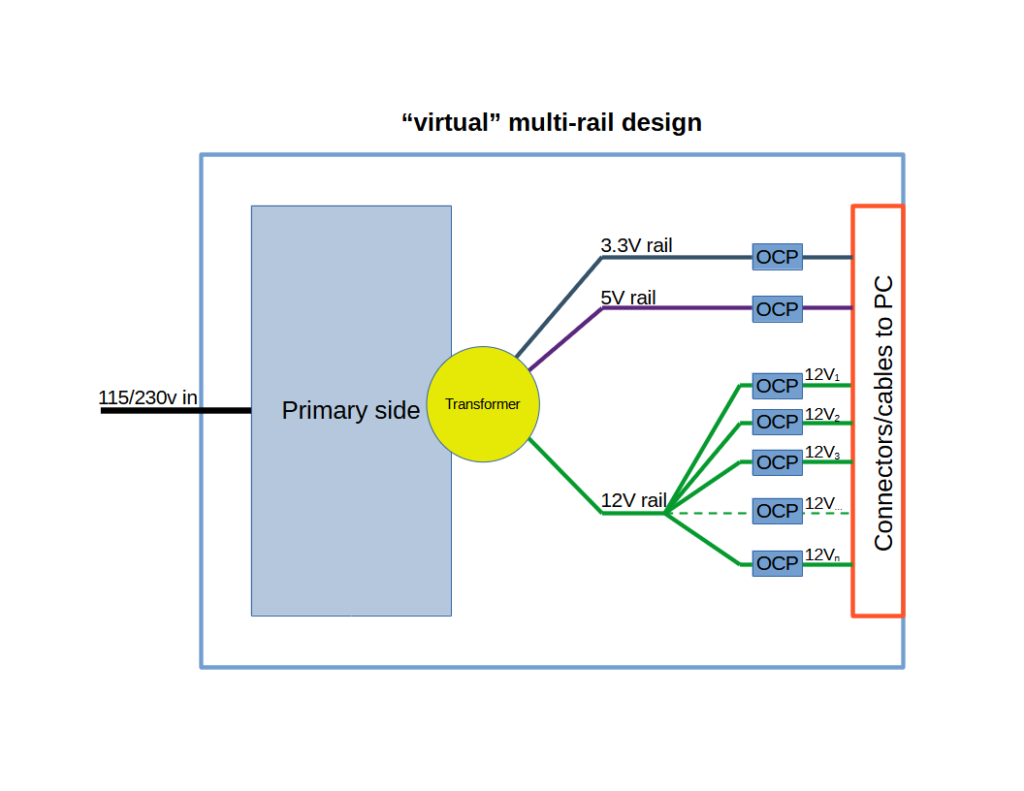
Note : OCP means Over-Current Protection. It monitors each rail and shuts down the entire system in case a rail is overloaded.
It is important to note that this does not mean one rail per connector or cable at the end, but rather that you can balance a few connectors per rail instead of every connector on a single rail.
That is the very basic of it. Pretty much all multi-rail units are advertised as such, and you should have some manual or guide to properly plug your cables if you own a multi-rail unit.
Should you worry about it ?
No. As said at the very beginning, it is just a different way to achieve the same result. A multi-rail unit has a slight safety advantage which is a plus, but otherwise it does not make a power supply better or worse than a single-rail. It does not change the behavior of the machine either. Both designs are made to be sure the computer works the same in the end.
In fact, your computer does not know if you use a single or multi-rail unit, and does not care. It only cares about getting its voltages properly and the correct amount of current to function.
The only important part of a multi-rail unit is making sure you don’t plug everything on a single rail to avoid overloading it.
Bonus : old physical multi-rail designs
One way of making a multi-rail unit is called the “physical multi-rail”, and it is exactly that : one full circuit per 12V rail or output. This is a very expensive method as every part is bought as many times as there are rails. There is also an issue of space with more and more parts crammed inside.
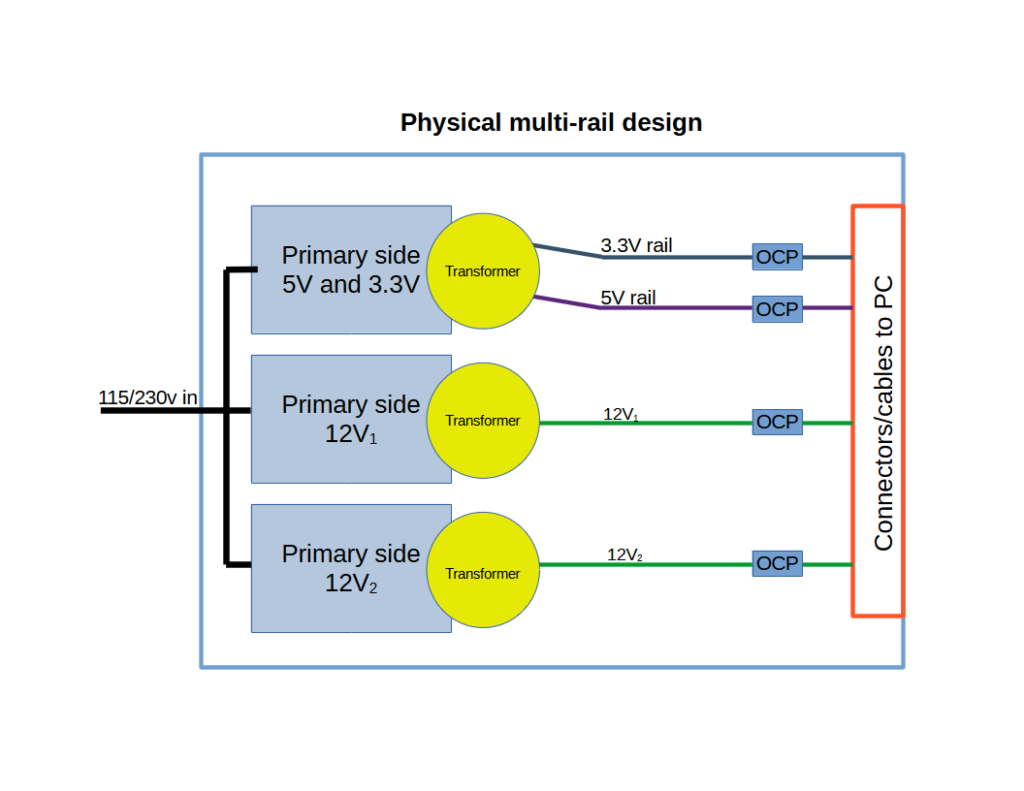
As a result, this method is very rare if not unused, and there is almost no physical multi-rail unit with more than two 12V rails. It is quite literally like shoving two power supplies into one. You double the 12V rail to make a second one.